diagnostics
- Home
- diagnostics
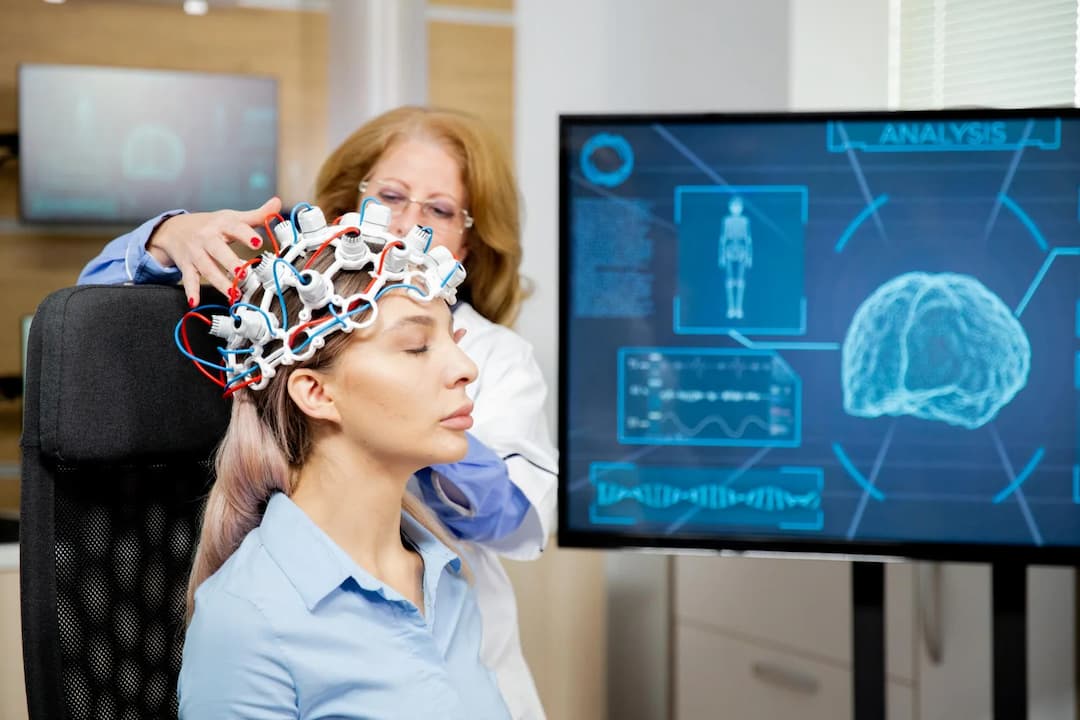
EEG (Electroencephalogram): EEG measures electrical activity in the brain by placing electrodes on the scalp. It is used to diagnose and monitor neurological conditions such as epilepsy, sleep disorders, and brain tumors. EEG captures the brain's electrical impulses, providing valuable information about brain function and activity patterns.
NCV (Nerve Conduction Velocity): NCV tests the speed and strength of electrical signals as they travel through nerves. This test helps diagnose nerve damage or dysfunction, such as peripheral neuropathy or carpal tunnel syndrome. By measuring how quickly and effectively nerves transmit signals, NCV provides insight into nerve health and guides treatment planning.
The referral letter is given to the patient from Vcare. Discount will be given to the patient based on that letter.
Read More
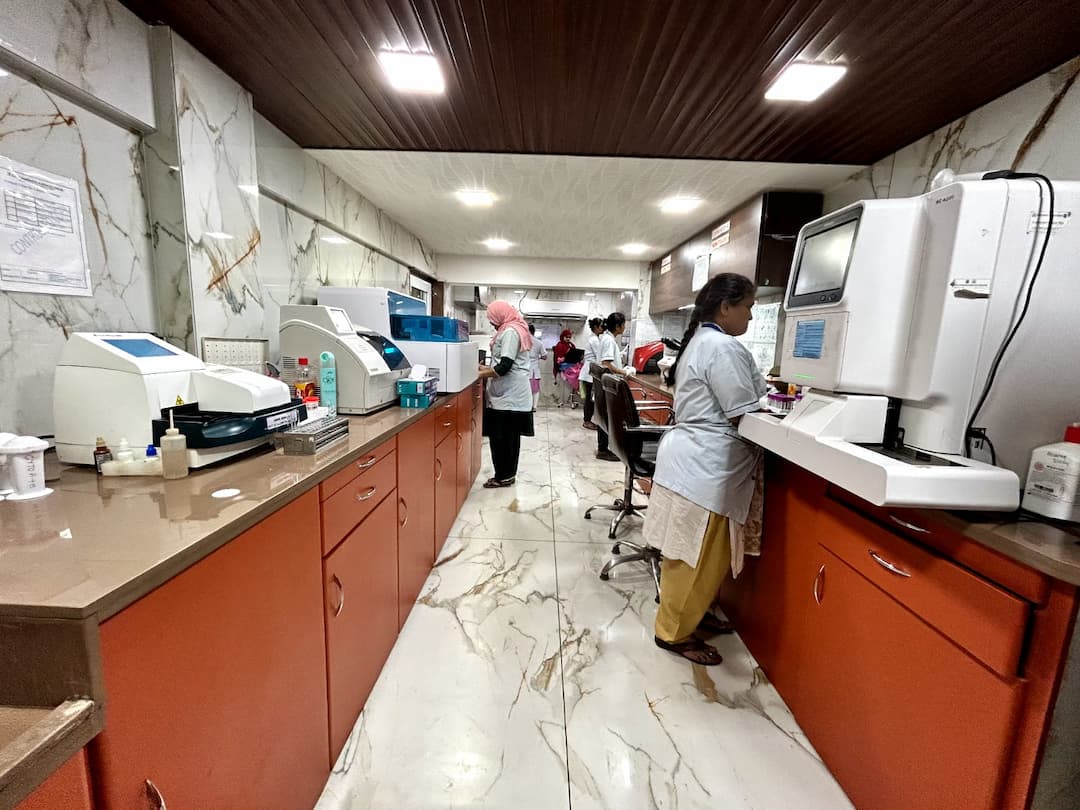

Vcare pathology laboratory is a NABL accredited lab. We ensures that our laboratory meet specific standards for quality and competence. All the tests are performed on fully automated Analyser such as RANBAXY 6 part BC 6200 cell counter, Mindray CL – 960i Immunoassay Analyser, BIORAD D-10 HPLC machine (USA), VITROS 250 Dry chemistry (USA), SYSMEX CA-101 coagulometer analyser, MINI SED automated ESR analyser, Minividas (France), Mispa i3 (nephlometry), Matrix Gel system for blood grouping, Fuji (Dry chemistry) & URI PLUS 600 urine analyser. We have well Experienced & Certified Medical Professionals, Including Pathologist, R Technologist. Meet International Standards For Quality And Competence. Have Robust Quality Control Measures In Place. Employee Qualified And Trained Personnel. Using Calibrated Equipment And Validated Methods. Participate In Proficiency Testing Programs. Results Are Reliable & Precise. Efficient Service To Ensure Positive Patient Experience. Ensure Robust Systems For Protecting Patient Data & Maintain Confidentiality. Maintaining High Standards To Deliver Reliable & Quality Diagnostic Services.
Read More

X-Ray imaging provides detailed internal views of the body by using electromagnetic radiation to capture images of bones and tissues. It helps diagnose fractures, infections, and tumors by highlighting differences in tissue density. X-Rays are quick, non-invasive, and widely used for both diagnostic and monitoring purposes. Advanced techniques, such as digital radiography, enhance image clarity and reduce radiation exposure. X-Ray imaging is essential in various medical fields, including orthopedics, dentistry, and oncology, to inform treatment decisions and track progress.
Read More

ECG, or electrocardiogram, is a diagnostic test that measures the electrical activity of the heart. By recording the heart's electrical signals, an ECG helps identify irregularities in heart rhythm, detect heart disease, and assess overall cardiac health. It is a quick, non-invasive procedure that involves placing electrodes on the skin to capture the heart's electrical impulses. ECGs are crucial for diagnosing conditions such as arrhythmias, heart attacks, and other cardiac disorders, providing valuable information for treatment planning and monitoring.
Read More
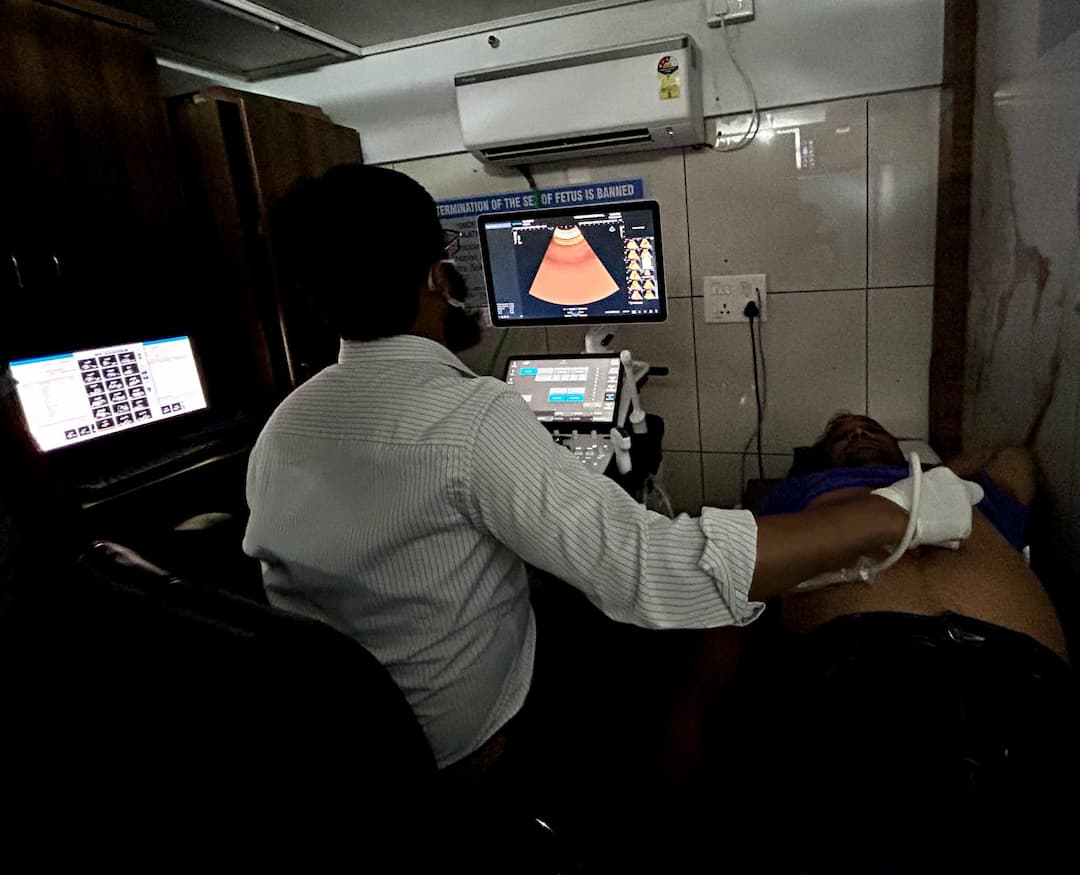
Sonography, also known as ultrasound, uses high-frequency sound waves to create real-time images of the body's internal structures. It is a non-invasive imaging technique that helps visualize organs, tissues, and blood flow, making it valuable for diagnosing conditions, monitoring pregnancies, and guiding certain medical procedures. Sonography is particularly useful for examining soft tissues and detecting abnormalities like tumors or cysts. It is safe, with no ionizing radiation, and provides immediate results, making it an essential tool in various medical specialties.




Read More

Mammography is a specialized X-ray imaging technique used to screen and diagnose asymptomatic women for breast diseases, particularly breast cancer. It detect tumors before they become palpable. Lump, pain, unusual discharge & history of breast cancer are at high risk.
Mammography has shown reduce breast cancer mortality by detecting cancer at an earlier stage. It involves compressing the breast between two plates to obtain detailed images of the breast tissue. Mammograms can detect abnormalities such as lumps, calcifications, and other changes in the breast before they can be felt. Regular mammography is crucial for early detection, which improves treatment options and outcomes. It is an essential tool in breast health management and cancer prevention.
Read More

OPG, or orthopantomogram, is a panoramic X-ray of the upper and lower jaws, teeth, bone structure, wisdom teeth, infections, tumors, and surrounding tissues. It provides a comprehensive view of the dental and skeletal structures in a single image, aiding in the diagnosis of dental issues, jaw disorders, and bone abnormalities. OPG is commonly used in orthodontics, oral surgery, and general dentistry to plan treatments, assess development, and monitor oral health. It offers a broad perspective with relatively low radiation exposure compared to traditional X-rays.
Read More

Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTs) are a series of tests used to measure how well the lungs are working. They assess lung capacity, airflow, and gas exchange by having the patient perform specific breathing maneuvers. PFTs help diagnose and monitor respiratory conditions such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and pulmonary fibrosis. It Assess the severity of lung diseases, Monitor the progression of lung diseases, Evaluate the effectiveness of treatments (e.g., medications, rehabilitation), Assess lung function before surgery, especially thoracic or abdominal procedures.
Read More

The Treadmill Test (TMT) is also known as a Cardiac Stress Test or Exercise Stress Test. It is a diagnostic procedure used to evaluate heart function during physical exertion. The patient walks on a treadmill while their heart rate, blood pressure, and ECG are monitored. It helps diagnose conditions like coronary artery disease and assess overall cardiovascular health. Diagnose coronary artery disease (CAD) or other heart conditions, Assess the severity of heart issues, Evaluate the effectiveness of heart treatments or medications, Monitor heart health in patients with known heart disease, Determine safe levels of exercise for rehabilitation programs.
Read More

CT scan, or computed tomography, is an advanced imaging technique that combines X-ray technology with computer processing to create detailed cross-sectional images of the body. It provides a more comprehensive view than standard X-rays, allowing for the examination of internal organs, bones, and soft tissues. CT scans are used to diagnose and monitor a wide range of conditions, including injuries, tumors, and internal bleeding. They offer quick, accurate imaging and are essential in emergency settings and for planning surgical procedures.
The referral letter is given to the patient from Vcare. Discount will be given to the patient based on that letter.
Read More

MRI scan, or magnetic resonance imaging, uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of the body's internal structures. Unlike X-rays or CT scans, MRI does not use ionizing radiation. It is particularly effective at visualizing soft tissues, such as the brain, spinal cord, muscles, and ligaments. MRI is commonly used to diagnose and monitor conditions related to the nervous system, musculoskeletal system, and internal organs. Its high-resolution images aid in accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
The referral letter is given to the patient from Vcare. Discount will be given to the patient based on that letter.
Read More

PET scan, or positron emission tomography, is a nuclear medicine imaging technique that provides detailed images of metabolic and biochemical activity within the body. It involves injecting a small amount of radioactive tracer into the bloodstream, which accumulates in areas of high metabolic activity. PET scans are particularly useful for detecting cancer, evaluating heart conditions, and assessing brain function. The images produced help diagnose diseases, plan treatment, and monitor response to therapy, offering insights into the body's functional processes.
The referral letter is given to the patient from Vcare. Discount will be given to the patient based on that letter.
Read More
